Covered warrant (CW) 09.02.2022
The basic knowledge of covered warrants that every investor needs to know
CONTENTS
What is the Covered warrant (CW)?
- A covered warrant is a type of warrant where the issuer is a financial institution. When issuing warrants to investors, the issuer will take security measures by purchasing the underlying securities on the market.
- There are two types of CW:
- Call warrants (profit in the direction of the increase of the underlying securities - deployed)
- Put warrants (profit in the direction of the decrease of the underlying securities - Not yet deployed)
- At the current time, according to the regulations of the Securities Commission and the exchange, securities companies are only allowed to issue Put warrants, exercised by European style and payment by cash
|
No |
The parameters |
Meaning |
| 1 | Type of CW | Buy CW (Call)/Sell CW (Put). At the current time, only Buy CW (Call) is allowed to trade in Vietnam |
| 2 | Underlying asset |
The stocks on the market in the list of VNX50, VN30, and HNX30, selected by the issuer as the reference basis for guaranteed CW |
| 3 |
Lifespan of CW |
The circulating time of the CW minimum is 3 months; the maximum is 24 months. |
| 4 |
Last trading day |
The last day that CW can be traded (2 days before the maturity date) |
| 5 |
Maturity date |
The last day that the CW owner can exercise CW |
| 6 |
The payment method of settlement |
Cash payment is the difference between the exercise price and the underlying securities price |
| 7 |
Exercise price |
Price for investors to execute the call of underlying securities when the CW expires. This price is predetermined at the time of purchase of the warrant and remains unchanged over time. |
| 8 |
CW price |
The amount of money investor spends to buy CW |
| 9 |
Payment price |
The average of 5 price trading sessions before the maturity date of the underlying securities. |
| 10 |
Form exercise of rights |
Stock or Cash |
| 11 |
Volume CW released |
Minimum 1.000.000 CW |
| 12 |
Conversion rate |
The number of CWs that investors need in exchange for a underlying stock. |
| 13 |
Style |
European/ American |
| Call Warrants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CW from issuer
For example, the CW is as follows: |
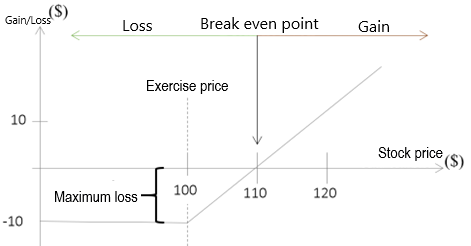 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
The common
- Trading market
The different
|
CW |
Stock |
|
|
Issuer |
Securities Company |
Business |
|
Time |
From 3 months – 2 years |
Until the enterprise is dissolved, delisted |
|
Trading |
Fee rights |
Buying stocks |
|
Securities company provides margin |
Not allowed |
Allowed |
|
Rights to business (Such as voting rights, the right to receive dividends, the right to buy additional issued shares, the right to receive bonus shares for the underlying stock issuer, ....) |
Don’t have any rights. All company’s events related to the CW's underlying stock (if any) arise, the warrant will be adjusted through the execution price and conversion ratio. |
Full rights of shareholders |
Compare CW with Future contracts
The common
- Value volatility based on underlying securities
- High leverage
The different
|
CW |
Future contracts |
|
|
Tổ chức phát hành |
Securities Company |
HNX |
|
Position for investors |
Call and Put warrant |
Long/Short |
|
Trading period |
T+2 |
T+0 |
|
Liquidity |
Has market makers. |
has no market maker |
Pros and cons of investing in CW
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
|
Step 1 |
Step 2 |
Step 3 |
||
|
Open securities account |
Have assets in your trading account |
Get started |

 18006277
18006277  master@miraeasset.com.vn
master@miraeasset.com.vn 